Artificial Intelligence in Poultry Industry. What Are the Latest Innovations in Poultry Farming?
Inside this article:
Meat consumption is a trending topic, mainly in the context of reducing its environmental impact and improving animal welfare. The poultry meat industry, which makes its global majority, is first in line when it comes to demand for innovation. As meat and egg consumption continues, artificial intelligence (AI) can help poultry producers tackle the abovementioned issues while also making the industry implement more ethical principles and processes. Are you wondering what exactly AI-based systems can achieve? Here’s our take on the potential of artificial intelligence for the poultry industry.
TL;DR
• Artificial intelligence (AI) can help the poultry industry address environmental impact, animal welfare, and production efficiency and also automate animal identification and weighing, improving accuracy and efficiency.
• Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) utilizes AI-based systems to monitor and control poultry production.
• AI can optimize breeding processes by automating tasks like egg grading, identifying live embryos, controlling incubation conditions, and predicting hatching probability.
• Global meat consumption, especially poultry, is increasing despite efforts to promote plant-based diets.
• Contact nexocode data engineers to harness the full potential of AI in the poultry industry.
Global Poultry Industry - Current State
Even though vegetarianism and veganism are on the rise, particularly in Europe and the United States of America, global statistics show our consumption of meat, particularly poultry, is rising. One of the reasons is that many countries that so far have been considered developing are jumping into the category of developed. The wealth level increases, and more people are able to afford food products like meat, increasing the world poultry production.
Promoting plant-based diets and cruelty-free alternatives such as lab meat is important, but on a global scale, it is little likely that these efforts will bring noticeable results. Meat remains one of the most accessible sources of protein and is a foundation of many cuisines worldwide, and that stands in the way of consumption reduction. Although it should remain one of the targets to reduce meat consumption levels, at this point, it is crucial to make the poultry industry work more efficiently while improving animal welfare and reducing epidemiological risk and pollution.
Poultry leads in the statistics, with global chicken meat consumption constituting a share of 43%, which in 2019 was equivalent to 14.7 kg per capita. (OECD UN data). In recent decades, poultry production has become much more regulated, forcing producers to improve their monitoring methods. That, together with the increasing demand, has fueled the development of Precision Livestock Farming (PLF), understood as a set of tools that facilitate livestock control with the use of advanced technology, including artificial intelligence. You can read more on AI-based systems that improve livestock production and management in our recent article on AI-Based Smart Farming.
Harness the full potential of AI for your business
Sign up for newsletterAside from software, PLF engages different elements that automatize the quality control process and gather data, such as cameras, microphones, sensors, and scanners. The system monitors the conditions and nutrition and animals’ responses to it, detecting sudden events at the same time and triggering actions as well as early warnings based on this data aiding better poultry production.
The Challenge of Digital Transformation in Poultry Farms
Even though in terms of environmental impact (particularly the CO2 emissions), the poultry industry is less harmful than, for instance, beef, it deals with other issues that urgently need solving. The most pressing is the rising demand that poultry producers need to cope with. The efficient solutions often come at cost of reducing the living space of the animals and lowering the level of their control. With technology, they can increase production while avoiding these problems to occur. AI can also suggest the most efficient space configurations and identify areas to unblock additional resources.
In the poultry industry, the animals are usually identified per flock, which may lead to quality control issues. Modern technology aims at breaking down this division and controlling animals individually, as it allows to detection of epidemiological risk much earlier and keep the track of each animal’s health and development. With artificial intelligence, such detailed identification is finally achievable without additional costs.
Applications of Big Data and AI in the Poultry Industry - Use Cases
Farmers can take advantage of the artificial intelligence potential in various areas of their activity, from welfare control to breeding optimization. We gathered the most promising use cases to give you a big picture of what a digital transformation can mean for a poultry production business.
Animal Identification
Identification is a pillar of all the monitoring processes that allow the farmer to maintain maximum control over the livestock. With artificial intelligence tools, manual identification systems can be fully replaced with automation, increasing control levels while reducing staff demand. The livestock producers usually use wing bands or leg bands for the sake of identification purposes. Other approaches include video identification. AI can detect individual animals and track them in video footage so that it can be used for this purpose as well.
The artificial intelligence-based system powered with computer vision can scan the barcodes or other identification signage and automatically identify each bird. This way, the poultry farm employees are capable of revising the particular bird’s history as all the collected data is attached to its “profile”.
Automated Weighing Systems
In the case of poultry, weighing isn’t as problematic as in the case of other types of livestock. The weighing usually does not cause the birds as much stress as the larger animals. However, they tend to be weighed in the flock, which creates some logistic challenges. An automated weighing system supported by cameras and an animal identification system with sensitive sensors can shorten the process of weighing to a minimum, making it much easier to obtain accurate measurements. They are automatically processed, saved in a database, and assigned to a particular flock (or an individual bird, depending on the system). This information serves various purposes, from health monitoring and tracking weight uniformity to regulatory compliance.

Poultry Welfare Monitoring and Detecting Chicken in Distress
Poultry Welfare Monitoring and Detecting Chicken in Distress
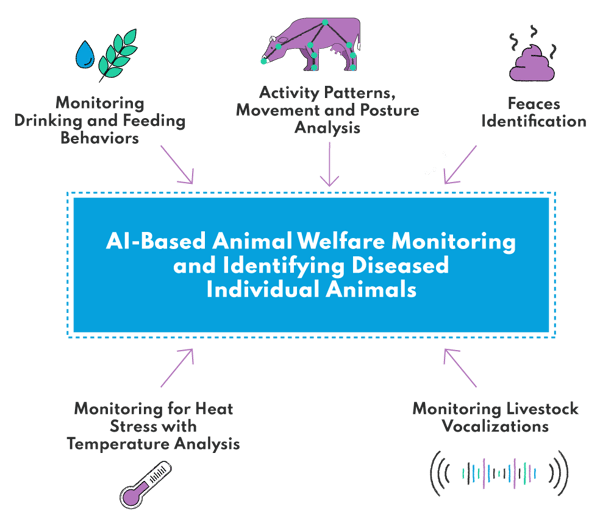
Welfare monitoring is essential from the ethical perspective (more and more emphasized by the customers) but also in terms of product quality assurance and epidemiological risk prevention. Artificial intelligence provides livestock producers with advanced monitoring tools that allow them to control the welfare of their animals and their response to various environmental factors. In which areas exactly can machine learning technology bring in additional value?
Monitoring Flock Feed and Water Consumption
Nutrition patterns are among the essential aspects to monitor in terms of quality assurance. The anomalies in this field are the first red flag that could imply health or behavioral issues among the birds. By gathering data in real time, the AI system paired with sensors and weighing or measuring d can trigger early warnings once any deviation from the norm is affected.
It may also find correlations between environmental changes and feeding/water consumption patterns. On their basis, livestock producers draw conclusions on practices that could improve animal welfare. At the same time, it allows them to track the flocks or particular birds that consume food above the norm and identify the reasons for it.
Activity Patterns, Movement and Posture Analysis
Movement and posture can also tell us a lot about animal welfare. Without technological tools, controlling these aspects would be very challenging, considering the number of birds and their concentration on poultry farms. However, artificial intelligence systems linked to cameras with computer vision can do all the job automatically.
The system, trained with the images of the correct postures and movements, can detect anomalies and link them to particular health or behavioral issues. It may, for example, issue an immediate warning once it detects movements that imply cannibalistic behaviors among birds in the real-time visual data captured by cameras. This issue, common in poultry farms, is hard to tackle in a traditional way, but with computer vision, it can be solved instantly, preventing bird loss.
Feces Identification
Feces are another thing that serves as a crucial bird welfare indicator. The automated system can analyze its properties with computer vision or, alternatively, verify the obtained samples, scanning the analysis results for any anomalies in the poultry chicken microbiota, such as the presence of unwanted bacteria.
Monitoring for Heat Stress with Temperature Analysis
In order to develop correctly and maintain good health, the birds need steady, optimized conditions. The temperature may affect animal welfare like no other variable. At the same time, the risk of significant fluctuations is the highest for temperature among all the variables. That’s mainly due to space limitations and the specifics of the poultry industry. Thus, it is essential to monitor the temperature levels in real time with the use of sensitive thermometers and sensors. The system receives the collected data and triggers automatic reactions when the norms are crossed, turning on the AC and ventilation.
Monitoring Chicken Vocalizations
Another variable that can be a great indicator of birds’ welfare is vocalization. They can tell the farmer a lot about the health of the flock and its behavioral issues. Just like image detection, AI-fuelled sound detection systems (usually with an SSL method - sound source localization) can identify anomalies and issue warnings on this basis. The machine learning model analyses the recordings in search of deviations from the patterns identified as correct in the training phase. With vocalization monitoring, the farmers can also prevent cannibalistic behaviors in the flock.

Optimizing Hatcheries and Poultry Breeding
Aside from controlling the birds’ welfare, artificial intelligence has an excellent proving ground when it comes to optimizing breeding processes. Automated systems can help livestock producers improve efficiency, but also eliminate controversial practices that would be a standard until recently. Here are some of the most significant use cases in the field of breeding and optimizing hatcheries.
Automated Hatching Egg Grading and Selection
The ideal egg with the highest health and hatching probability is clean, free of cracks, has the correct shape, and is within the acceptable weight range. Ideally, these eggs should be chosen manually for incubation. However, the number of eggs produced on poultry farms today is so vast that it’s impossible to grade them all without technology. Fortunately, the latest developments in computer vision make it possible to automate this process with high precision.
Eggs are graded according to their external features and weight. The system can work in real-time or batch mode and select the eggs that have the highest hatching chances while discarding those with a low probability of success. This significantly reduces wastage and improves hatchery efficiency.
Identifying Live Embryos in Eggs
Modern technology enables poultry farmers to avoid wasting resources on keeping infertile eggs inside the hatcheries. By engaging near-infrared hyperspectral imaging techniques, they can separate the eggs that contain live embryos from the infertile ones at the very early stage. The technique, combined with machine learning technology, and more specifically, a classification ML algorithm, provide them with detailed insights which get more precise with time due to received feedback.
Automatic Incubation Process Control
The incubation process is another area where machine learning can be of great help. The conditions during this phase have a significant impact on the final quality of the chicks. Thus, it’s crucial to maintain the temperature and humidity at an optimal level and ensure that the eggs are turned regularly.
In the past, all these processes were carried out manually. Nowadays, however, there are automatic incubators that can do all of this by themselves. The incubators use sensors to monitor all the critical parameters and ensure they remain within the desired range. They also have egg-turning mechanisms that work automatically. The entire process is overseen by computer software that can be powered up by additional machine learning algorithms to predict hatching probability and improve with time.
Monitoring Embryos Development
For the embryos to develop correctly, the conditions should resemble those they would receive in the natural environment. Any fluctuation in temperature or humidity may affect their development negatively. Aside from monitoring the conditions, artificial intelligence paired with computer vision can also help the producers monitor the embryo’s development itself.
That’s possible thanks to the time-lapse imaging system that the incubators in the hatchery can be equipped with. The machine learning model evaluates the captured images in search of anomalies and classifies particular eggs as developing correctly or incorrectly. Based on this output, the hatchery managers can decide what to do with the embryo and try to bring its development back on track with appropriate changes in conditions.
Sex Determination
The next use case we want to discuss has great potential to solve one of the most pressing issues the poultry industry is facing today. Every year, billions of male chicks get killed right after birth on poultry farms worldwide (just in German breeding farms, it is over 100 million birds per year, according to Bayern data). Advanced sex determination techniques could finally end this controversial practice while allowing the hatcheries to work even more productively at the same time. That’s because they could entirely remove male eggs from the incubators.
How can the farmers determine the sex of the embryos? Modern systems use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) supported by machine learning classification models that separate the male embryos from the female based on visual data. Flocs with different colors of male and female chicks can be sexed with infrared egg scanning and machine vision. Image evaluation and classification are completely automatic. Other methods include endocrinological gender identification.
Predicting Hatching Probability and Efficiency
The entire hatching process should be as efficient as possible to avoid any delays or disruptions. The machine learning algorithm helps the hatchery staff to predict how many eggs will hatch and when they are going to do it. Based on that, the workers can schedule hatchery plans to ensure everything goes smoothly.
Detecting Breeding Times and Reproduction Monitoring
Another way to improve breeding efficiency is monitoring the breeding times. In order to estimate the best breeding time, the machine learning algorithm combines the flock age, heat times of the monitored female birds with the other variables that impact fertility (like environmental conditions, stress, etc.).
Identifying High-Value Breeding Stock
Machine learning algorithms and computer vision can also help livestock producers identify high-value breeding stock in order to maximize profit and production efficiency. Based on previously identified relevant traits, the breeders are capable to estimate the potential economic value of a particular animal. The score it receives may be a combination of genetic features, visual traits, and health history data. The ML model takes all these aspects into account, pointing out the high-value breeding stock.
Chicks Quality Control
Eggs aren’t the only ones that need to be monitored in poultry houses — the quality of chicks is also essential. Computer vision systems can identify chicks that didn’t develop properly. To support disease management and food safety perspective, machine learning models analyze their appearance and posture to determine sick chicks. Based on that, they decide whether a chick is healthy or not and needs to be removed from the population.
From the husbandry and welfare perspective, those chicks often die soon after they’re born, but sometimes they may also suffer and die a slow and painful death. In both cases, it’s crucial to remove them from the population as soon as possible with smart automation systems.

Improving Poultry Houses and Hatcheries
Predictive Maintenance of Farm and Hatchery Equipment
Poultry farmers need to maintain their equipment in good condition to avoid any unexpected downtime and disruptions. However, it is not easy to track the status of all machines manually, especially in larger facilities. This is where predictive maintenance comes into play.
Predictive maintenance is a technique that uses machine learning to predict when a particular piece of equipment is going to fail. By doing so, the farmers can schedule the necessary repairs or replacements in advance, before the equipment breaks down completely. As a result, they can avoid costly downtime and keep the farm running smoothly.

Post-Farm Activities for Improved Poultry Processing and Egg Production Efficiencies
The role of AI does not end in the poultry broiler and layer farms. The poultry processing plant units can also use it further in post-farm activities to ensure the highest quality of their products and reduce epidemiological risk or prevent breaking quality regulations.
Ensuring Food Safety
Every poultry producer has to comply with strict food safety norms imposed by the controlling organs on different levels - from the local to the EU ones. A trained algorithm equipped with a computer vision system can evaluate the products on the assembly line in terms of regulatory compliance and sort them based on the result of this evaluation. With time, the accuracy of the classification model will continue improving as it receives more and more feedback.
Improving The Efficiency of a Processing Plant
From the food processing perspective, implementing machine vision in processing plants has already helped to improve the removal of feathers, skin, and subcutaneous tissue. AI can help in the analysis of the structure and density of tissues to differentiate meat versus bone in order to trim meat precisely. The result is a more efficient use of resources while ensuring better product quality.
Egg Packing
Another application of machine learning in egg production is sorting eggs by weight and grade. The classification models can automatically handle this task with great accuracy, increasing the whole process’s efficiency.
Improving Food Supply Chain Management
Artificial intelligence can also contribute to streamlining the food supply chain. The livestock producers can use it to estimate the demand with predictive analytics and adjust their production volumes to these estimations. Such adjustments are particularly important in the meat industry due to their environmental impact as well as ethical questions. As it’s dealing with alive creatures, any production excess should be avoided by all means. At the same time, poultry is a product with a short shelf life, so accurate demand estimations are crucial for the sustainability of this industry.
Identifying Inefficient Farms
Trying to improve the efficiency of chicken farms is a never-ending task. There are always new ways to make the process more efficient, whether it’s by using AI or some other technology.
From a production standpoint, chicken producers or other large food conglomerates can use machine learning to identify inefficient farms and find out what needs to be improved. By analyzing data such as feed conversion ratio, water usage, energy consumption, and others, laying efficiency, and hatching, the system can pinpoint which farms are performing below average and need attention.
This way, the farmers can focus their efforts on making the necessary changes and improving the efficiency of their chicken farms.
Benefits of Applying Machine Learning in Poultry Farming and Egg Production Sectors
The examples above prove that artificial intelligence can be a motor of positive change for poultry houses, making poultry operations more efficient, productive, sustainable, and safer, streamlining disease management.
At the same time, it has the potential to end ethically controversial farm management practices that animal rights activists are drawing attention to. Plus, it improves the birds’ welfare, which results in a better quality of the products and lower epidemiological risk.
Happy, healthy birds also do not need so many antibiotics and other medicine, which contributes to their value and helps the producers fulfill the requirements of the regulatory organs and meet the expectations of their customers.
Bringing Artificial Intelligence to the Future of Sustainable Poultry Production
As a software house with deep expertise in artificial intelligence and machine learning, we help companies from various industries transform into AI-driven market leaders. Having worked with diverse businesses, we know how to identify their issues firsthand, and we have successfully solved some with the support of machine learning techniques. If you see the potential for your business in them, reach out to us anytime. We can discuss any aspects and use cases listed in this article through the prism of your company’s specifics and goals.