Get the Most Out of Natural Language Processing in Retail, eCommerce, and Marketing: Use Cases and Benefits
Inside this article:
As artificial intelligence (AI) begins to play an increasingly important role in our lives, one of the most promising applications is natural language processing (NLP). NLP allows machines to interpret and understand human language, making it possible for them to carry out a wide range of tasks such as translating text, answering customer service queries, or even carrying out complex marketing campaigns. In this article, we will explore the use cases of NLP in retail, eCommerce, and marketing and discuss the benefits of using this technology.
What Is Natural Language Processing, and What Tasks Can It Handle?
Natural language processing is a branch of computer science – specifically, artificial intelligence – that enables machines to understand human language. From the algorithm’s perspective, written text or record containing natural language (understood as human language) isn’t comprehensible at all. The machines cannot make sense of it unless they learn how to do so with the NLP techniques. With advanced natural language processing, they can comprehend the meaning of text and speech in all its complexity, catching context, discourse, sentiment, or irony.
For it to be possible, the content has to be first broken down into segments and words and turned into numeric tokens. In the next step, the programmers reduce these tokenized words into their word stem or root. These processes are called respectively, stemming and lemmatization, and they have critical importance to the results of the NLP, particularly in the case of languages with a complex inflection, such as Polish. They may also use speech tagging, a learning technique you most likely know from school that links the words with particular parts of speech.
After the content is stripped down to parts and sequenced, the neural network can process and interpret it. And that’s where the magic happens! At its current stage of development, NLP is already very sophisticated thanks to deep learning, enabling the machines not only to decode the surface meaning but also to go much deeper, finding contexts and emotions hidden between words.
NLP Tasks
The spectrum of the tasks natural language processing can handle is broad. Many of these are the backbone of the processes that help us in everyday life, like automated translation or autosuggestion. The most common tasks across industries include:
- Named Entity Recognition
As the name suggests, it’s a process of identifying named entities (like a person, company, location, etc.) in text or speech.
- Keyword Extraction
This task serves for extracting the most relevant phrases from the content. It streamlines other, more complex tasks and is a foundation of any digital document management system.
- Content Summarization
To generate a summary, the programmers can go either for an extractive or abstractive approach. In the case of the first one, the summary is composed of the original text, and the second one involves new text generation.
- Topic Modeling
This task serves for scanning an unstructured dataset (for example, a set of documents) for repeating phrases and expressions and extracting topics to which the fragments of the content are attributed with the clustering method.
- Sentiment Analysis
This NLP technique enables extracting and classifying emotion contained in the speech or text. Usually, classification involves three categories - positive, negative, and neutral, but it may be more extensive if necessary.
- Text or Speech Generation
With changing market requirements shaped mainly by the marketing and e-commerce industries, a strong emphasis is recently being put on content generation. This task is much more complex and requires the use of neural networks made specifically for generative purposes.
The Growth of eCommerce and the Challenges in the Retail and Marketing Industry
The e-commerce market has been gradually growing in the last decade, but it’s the pandemic that made it gain real momentum. Only in 2020 (the first year of the pandemic), the e-commerce sales increased by 43% ( ARTS 2020), and it continues to grow even though the crisis is now over. That, of course, had caused the shift in customer expectations and increased pressure on the retailers.
With the growing amount of transactions, returns, complaints, and other kinds of customer inquiries, the retailers started to reach out for advanced automation in order to gain a competitive edge. NLP is one of the techniques that enables them to cope with the dynamically changing market requirements and provide the best experience to their clients. How? Streamlining the processing of inquiries, automating customer service, and many other ways are covered further in this article.
When it comes to marketing, a similar shift could be observed in recent years. As the market is getting increasingly competitive and e-commerce-oriented, it’s becoming harder and harder to stand out in the digital crowd. The search engine providers do not help the digital marketers, constantly refining their algorithms. The techniques that would work perfectly just a few years ago now bring no results. It’s also much more challenging to catch the customer’s attention.
With NLP, the marketers can improve their targeting, gather better insights, and personalize the content and communication, which provides them with an advantage over the competitors. The most complex natural language processing tasks, like text generation, also help them win the content battle and keep their actions efficient while gaining favor with search engines.
Natural Language Processing Applications in Retail, eCommerce, and Marketing
Whereas in insurance, banking, and related industries, NLP streamlines mainly the internal processes, like fraud detection or documentation processing, in e-commerce and marketing, its main applications are customer-oriented. Let’s take a look at the most exciting examples of those.
NLP in Retail and eCommerce

Semantic Search Engines
Contrarily to lexical search, the semantic search denotes the actual meaning of the entered search phrase instead of matching it with the most exact results. It aims at identifying the intent of the person sending the inquiry. From the perspective of an e-commerce business owner, this type of search facilitates access to users who don’t necessarily know what they are looking for.
Semantic search is not always applicable. For example, if someone types: wool coat black X brand, all the engine needs to do is identify relevant keywords and find the match. But when the search queries are vaguer – for instance, when someone types casual outdoor clothing instead - it works perfectly.
Voice Search
A few years ago, it would seem unlikely that we could switch to voice commands so easily. But here we are! Today, the users rely on voice assistants for many everyday tasks that involve mobile devices (and not only). Voice search is possible thanks to NLP, which can transform speech into text for the user wanting to find a particular product via a search engine.
To generate organic traffic with this particular channel, e-commerce retailers can use voice-oriented optimization. There are different strategies for that, but the majority involve using less formal and more natural language in keywording (we speak in a different way than we write) and long-tail keywords.
The e-commerce businesses can also enable voice search in their stores, making it possible for the users to search without typing. Such a feature is likely to cause a positive shift in user experience if it reflects the options the user has when searching in a traditional way (search by color, search by name, autocorrect the misspelled names, etc.). Let’s not forget the inclusivity aspect – the shops that enable voice search are more inclusive since the visually impaired users can navigate through them without any issues.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is a powerful tool for retailers in an increasingly competitive market since it enables them to gather insights quickly and efficiently, even if they receive numerous reviews every day. Without NLP-based tools, it’s hard to make the most out of the feedback. Reading every review would be counter-effective, and extracting actual data in a broader context out of all this content – is practically impossible.
With sentiment analysis, the retailers can get a big picture of the market reception of their products and services. The machine learning algorithm classifies the customer feedback as positive, negative, or neutral based on extracted keywords or expressions that were previously identified as indicators for a particular category.
However, the feedback hides in other customer data, too – messages, comments, etc. In their case, the programmers need to take a step further and identify the intent of the content first, best with the contextual semantic search that provides the most accurate results. This method doesn’t rely on keywords but on the contextual relationship between the words, which makes it more probable to decode the actual intent.
Efficient Customer Support for Processing Customer Queries
Seamless customer support is essential for e-commerce businesses in these competitive times. With natural language processing, they can streamline the query processing by categorizing the inquiries and adding priorities based on the content.
The model can extract keywords that imply which department the query should be directed to, and identify intent with contextual analysis. The most standard queries can go straight to the bot, which processes the content and generates answers with NLP. The more complex/ non-standard ones, on the other hand, can be sent to real-life consultants.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Chatbots are a flag, the most recognized applications of NLP. With the development of artificial intelligence, the interactions with these are becoming increasingly seamless and natural. That’s due to the usage of complex neural networks which can mimic human behavior when interacting with the typed text in natural language.
Bots are learning faster and faster, and that’s good news for retailers which spend a lot of money on customer service due to processing refunds, returns, and other e-commerce-related matters. With chatbots trained with the content of the solved queries, they can reduce the tasks their customer agents have to deal with in their daily work. While the customer support staff focuses on more demanding issues to solve, the chatbots answer the most common questions in an automatized way. Applying contextual semantic search may help to improve their answers’ accuracy, since it makes it easier to read the customers’ intent.
When it comes to virtual assistants that we use in everyday life, it’s essential for the retailers to optimize their stores for speech search which we have described above. And the bots are more and more commonly becoming a sort of virtual assistants as well, being able to solve complex problems of the customers, provide them with suggestions, or guide them through the purchase process.
NLP in Marketing
The specialists need to take the popularity of NLP-driven virtual assistants into account when creating their marketing strategies, preparing content that reads well also in text-to-speech mode. As the voice search is gaining popularity, they also need to rethink their approach to optimization. But NLP also creates opportunities for the digital marketing team – here are some of the most interesting examples of such.

Content Creation with GANs
A few had expected the AI would be able to beat the humans in writing, but the recent advance in this field proves it wrong. The GANs bring natural language generation to the next level, enabling artificial intelligence to generate perfectly sensible and coherent text twin similar to the ones created by humans. They can actually have an artistic value and even be funny or ironic!
What exactly is GAN? In a nutshell, it is a supervised approach to training generative models. It uses two sub-models – the generator and the discriminator – that compete with each other in terms of accuracy, which translates into great results. In the field of content generation, the GPT-3 (3rd generation Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is definitely a game-changer. With its extensive size, this neural network is able to create content that embraces all the complexity of the human language.
Nowadays, when the pressure on valuable content is increasing, both from customers and the search engines, content generation can become a significant part of an efficient content marketing strategy while also supporting search engine optimization.
Search Engine Optimization
NLP technology is a powerful tool for SEO specialists and marketers, enabling them to navigate through the complexity of the website content without wasting time. Using the entity extraction technique, they can identify the words worth linking (like names of the locations, famous figures, and proper names) to improve the link structure on the web pages.
Entity extraction also helps them make the website more navigable with the system of smart redirections. By extracting entities that describe their website and classifying them, they can also speed up the search engine indexation to generate more organic traffic. With AI-fuelled tools, they can also identify the best combination of short keywords, long tails, links and other elements that will strengthen their content marketing efforts.
Automated Summarization
Using NLP to summarize the content makes the marketers’ life easier, helping them monitor the media and competition in a faster and more effective way. Instead of reading every publication from cover to cover, they can just look through its extractive summary that gives them an overview of the content. They can also use it for the purpose of identifying relevant content or extract entities from the summaries in order to identify trends.
How Sales and Marketing Businesses Can Benefit From AI?
Natural language processing and other artificial intelligence techniques make it possible for the sales and marketing teams to automate a part of their work while they focus on more demanding tasks.
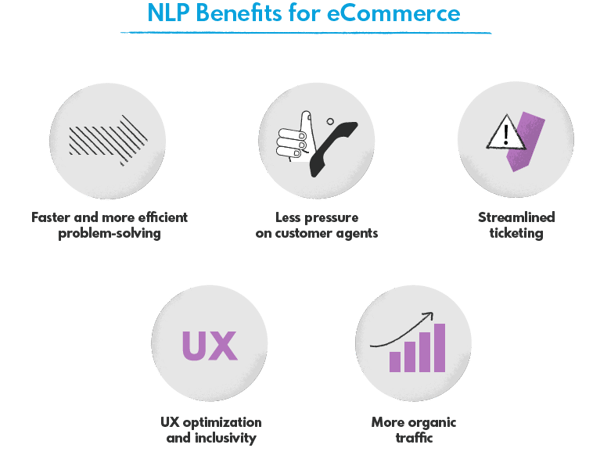
At the same time, they allow the companies to keep up with the evolving habits of their customers, who increasingly rely on virtual assistants and voice search. Since they meet their expectations, the customer experience improves, particularly among visually impaired users that often rely on this form of Internet navigation.
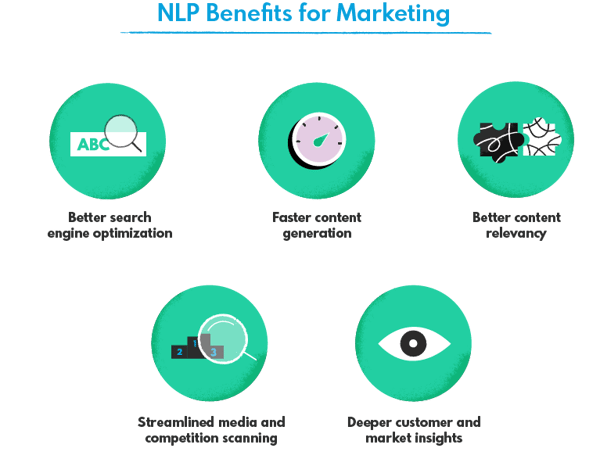
The impact natural language processing-based tools have on the efficiency of customer service is also not to be missed. NLP is thus a great tool to shape good brand perception while improving sales statistics at the same time.
NLP Applications – Where to Start?
When applying NLP to your project, the first thing to do is usually decide whether you can use an already existing tool (ready-to-use AI solution) or you would need to approach the project with custom NLP software development. Generic use cases usually will have off-the-shelf products available, but for specific solutions and higher accuracy and performance levels, you would need custom AI development services. No matter what you will choose, you still would need some level of integration and customization with other tools that you use.
For customized or custom solutions, you’ll also need to pick a sample dataset – either by gathering data on your own, which is more time-consuming or by finding an open-source dataset that matches your needs. Of course, the more extensive it is, the higher accuracy you can count on.
Then it’s time to use natural language processing techniques to break down the data for the model – but that’s something we will take care of!
If you would like to use natural language processing in your next project or are simply curious about its possible applications in your industry, reach out to us!