Industrial AI: How Artificial Intelligence is Revolutionizing the Manufacturing Industry?
Inside this article:
The manufacturing industry is under pressure. Labor costs are rising, while customer demand for faster, more customized products continues to grow. At the same time, the industry is being disrupted by a new technological wave: artificial intelligence (AI). AI has already begun to revolutionize manufacturing, and the impact is only going to increase in the years ahead. AI has the potential to revolutionize how we produce goods and services, making factories smarter and more efficient.
In this blog post, we will explore how industrial AI is changing the face of manufacturing and discuss some of the benefits it offers businesses.
AI in Manufacturing
AI has enabled rapid progress of manufacturing in recent decades, making the factories less labor-dependent and more efficient than ever. The introduction of machine learning was a milestone for this sector – the machinery, until then entirely dependent on the programming, would now be able to make its own decisions based on data.
Today, the applications of AI in manufacturing are numerous – from advanced predictions through quality assurance to waste reduction. We use artificial intelligence for planning, scheduling, optimization, robotics, and machine vision. Not only does AI provide the manufacturers with increased capacity and space for business growth, but it also gives us hope for a greener and more comfortable future.
How Industrial AI is Revolutionizing Manufacturing Operations - Top AI Use Cases in Manufacturing
You already know that artificial intelligence has great potential – but what about its practical applications? We’ve gathered some examples to illustrate how the manufacturers can benefit from machine learning and apply these algorithms in practice.
Production Optimization
Since the industrial era, manufacturers have been aiming at optimizing their production according to the infinite growth principle. The fundamental imperative is to produce more, faster, and at lower costs. Artificial intelligence can identify inefficient processes in terms of production volume or energy use in order to minimize waste and reduce costs. In addition, robotic assembly lines fuelled by AI can bring productivity to the next level, reducing the number of human errors and speeding up the manufacturing processes.
The optimization wouldn’t be possible without thorough planning. Before the automation entered the game, the manufacturers would mainly rely on the static Excel files to plan the production – but such a method would freeze the planning for some time, making them unable to react to changing variables like, for instance, downtimes in the supply chain. With the AI algorithms, they can automatize the planning and react to changes in real-time.
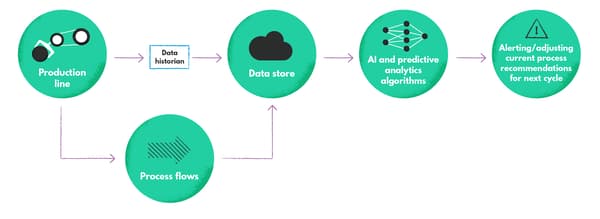
Related case study: Pharmaceuticals Production Process Predictive Monitoring
To improve the current repeatable batch production processes, a producer of pharmaceuticals approached us to implement AI models and utilize predictive modeling.
Our challenge? Building a model that analyzes real-time data streams from the production process and identifies potential outliers that may lead to deterioration of quality, based on historical data. The benefits are improved effectiveness, predictability, and efficiency of manufacturing operations and yields. Read more about this case study.
Predictive Maintenance
Every downtime is costly. Once it occurs, the manufacturing capacities of the factory shrink or even drop to zero, causing financial damage. Plus, getting back to the previous efficiency levels takes time. Even the shortest production stoppage may result in lowered quality, making the first batch of the product unsuitable for the market.
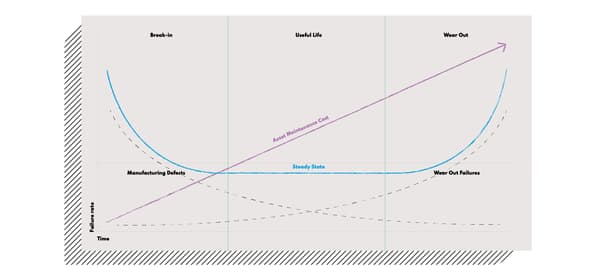
To avoid such scenarios, the manufacturers would schedule regular maintenance. However, with AI, they don’t have to rely on it anymore. Intelligent systems can detect and identify mechanical or electrical failure before the issue escalates to a full-blown downtime based on many machine data points that track equipment efficiency.
After detecting an issue and classifying it, they use automated protocols to prevent the problem from escalating and trigger alerts. You can go a step further, taking advantage of the power of predictive maintenance and estimating the probability of the machinery failure (with regression approach) or even its time (with classification approach).
Waste Reduction
With an increasing emphasis on sustainable production on worldwide markets, waste reduction is becoming one of the manufacturers’ priorities – and artificial intelligence is irreplaceable in this field.
First, it can serve research purposes, allowing the companies to come up with new materials that carry desirable properties while being biodegradable or fully recyclable. In addition, it can help them optimize the usage of resources to minimize waste.
They can achieve that goal through efficient material treatment on the production line, as well as downtime reduction with preventive maintenance described above. That’s because a big part of industrial waste is the low-quality products not suitable for the market use, and downtimes can contribute to periodical quality decrease. So can the defects in machinery or the production process, easily detected by artificial intelligence.
Energy Efficient Manufacturing
Manufacturing is responsible for a big part of energy consumption worldwide and thus, improving energy efficiency is one of the most crucial roles of AI in this sector today. To stop climate change, we’ll need to switch to fully renewable energy sources sooner or later – but meanwhile, we can try using the energy in a more thoughtful, sustainable way.
AI systems can help the factories detect inefficient processes that waste energy, like defects in machinery that cause leaks, a bad regulation of the heating system, or inefficient lighting. For instance – depending on the weather conditions and the distribution of the windows, some areas of the factory may heat up more than others. An intelligent control system can activate and regulate the air conditioning and heating based on these variables, reducing energy waste and improving comfort at the same time. The same goes for lighting. Switching to energy-saving LEDs is essential, but the factories can take a step further and automate it. Intelligent light distribution, maintenance-free brightness adjustment – these AI-fuelled features can lower the electricity consumption by more than a half. And, at the same time, they reduce the number of human errors.
Quality Control - Detecting Defects
The quality of the product depends on various factors, from design to the state of the machinery. The defects of the equipment, metal fatigue, human errors, breaks in production – all these variables may have a negative impact on it. The manufacturers may take various steps involving AI to avoid these issues, including preventive maintenance, which we have already described in the previous paragraphs. Still, the algorithms may not be efficient enough to prevent all events that lead to quality loss.
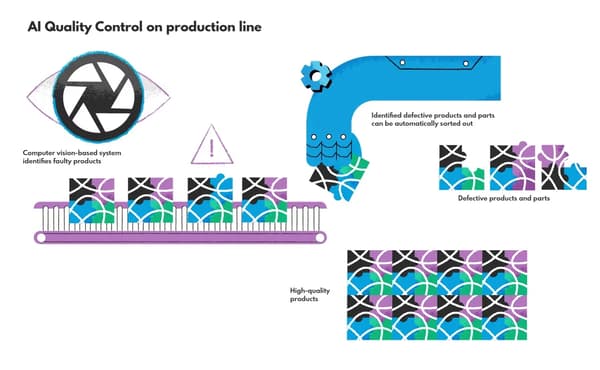
Using visual inspection, the manufacturers can keep an eye on the quality in the most efficient way – with the help of machine learning algorithms. Computer vision is developing at a fast pace, already enabling advanced defect detection without hiring additional manufacturing and quality engineers. How does it work? Speaking briefly, the sensing device sends the image to an interpreting device where it’s analyzed by AI algorithms (most commonly, neural networks) trained with datasets containing defect examples and images of flawed/unflawed products. Computer vision technology can detect holes, abrasions, scratches, undesirable shapes, and so on. With its help, the factories can maximize the product quality and its lifespan, improving customer experience and reducing waste.
Improving Safety on Production Floor
Manufacturing companies can use AI in various ways to improve safety on the production floor. The first example of such application - already mentioned in the context of energy efficiency - is lighting automation. Using it, they can respond to real-time demand for lighting, brightening up particular areas once it’s needed. Tracking defects and leaks with preventive maintenance algorithms also fall under this category.
The manufacturers can use computer vision to detect potential issues in the facility. Once the algorithms identify an anomaly, they send an alert via text message or app to the authorized representatives who can investigate the issue. The system may also trigger automated safety responses.
Visual inspection powered by machine learning algorithms can also track whether workers on the production floor are wearing safety gear and adhere to health and safety regulations. If not, they can send a message to a supervisor or sound an alarm. The technology can also monitor the workers’ fatigue levels and take necessary measures if they appear to be exhausted.
Supply Chain Management
They say forewarned is forearmed – and in the manufacturing industry, this expression is very relatable. To keep the production optimized, the manufacturing companies should not only follow the changes in supply chains or order deadlines, but also prepare themselves for various scenarios. The pandemic has proven that manufacturers have been underestimating the power of simulation. Many companies broke down with the crashing market because they didn’t prepare for the unstable supply chains.
Modern advanced planning and scheduling systems enable the factories to simulate unlimited cases and create scenarios for such eventualities. Even with a large, qualified team of researchers, analyzing all the possibilities manually would be impossible. Using the AI, the manufacturers can answer the “what if” question in no time - all they need is an extensive, quality dataset.
Predicting Demand
Manufacturers around the world have been using enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems for a long time already in order to optimize the usage of resources and maximize profit.
Even though these systems have empowered the companies, making space for advanced optimization, they’re far from being perfect. Since their calculations rely on constant parameters and the infinite capacity principle, they do not allow the manufacturers to make realistic predictions. They usually ignore the changing variables like the fluctuating demand. That forces the companies to play safe instead of adjusting to the changing market.
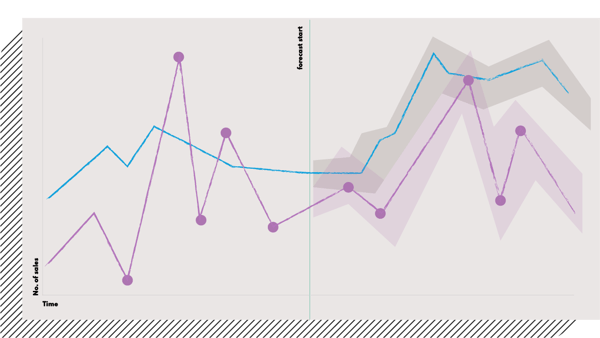
With the pandemic, many manufacturers have started noticing that such a planning model will not take them far in the long run. Even during a relatively stabilized period, the demand for the products can fluctuate, and the planning systems should take these changes into account. Modern APS systems fuelled by artificial intelligence update the production plan based on real-time data, reacting to these changes on an ongoing basis.
This way, the manufacturers can prevent overproduction, which has various negative implications. Aside from avoiding environmental issues and financial loss, it allows the manufacturers to save precious storage space. Using the machine learning models, they can plan the production ahead of time, taking the demand into account. The forecasting methods may involve neural networks as well as regression analysis, SVR, or SVM.
Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
The use cases above prove that AI has immense potential in the manufacturing sector. Of course, the manufacturers themselves can benefit from its implementation - but so can the economy and environment.
To summarize - for the companies, implementing AI-based innovations is an opportunity to:
- optimize the manufacturing process
- optimize process parameters
- reduce operational costs
- reduce waste
- reduce the carbon footprint
- increase safety
- improve product quality
- improve inventory management
- prevent downtimes
The Future of AI for Manufacturing
According to the predictions, artificial intelligence will continue to automatize manufacturing processes, reducing the workforce demand and boosting production. In the long run, it may shorten the working week and create new job opportunities.
Contrary to common conviction, the evolving AI doesn’t make the number of vacancies in manufacturing shrink. The manufacturers may not need as many employees on the production line as they would in the past – however, as they’re moving towards a data-driven business model, they will search for more analysts and data scientists.
With the current contribution of the industrial sectors to waste production and energy consumption, making the manufacturing processes more sustainable is the priority – and AI and machine learning can help us get there with its pattern-identifying ability. Manufacturers can use it to reduce their carbon footprint, contributing to a fight against climate change (and adjusting to the regulations that are likely to get even stricter). And since AI can significantly reduce operations costs, they invest more in process improvement resources, becoming more and more effective over time.
If you’re interested in implementing AI for your organization, get in touch with us. We can help you identify the areas for improvement and bring to life the benefits of AI and machine learning for your business. Let’s talk!